Sustainable Future: The Path of Solar Panel Recycling in Australia

Steve Hill
Expert in Residential and Commercial Solar Solutions and Energy Efficiency
4 min read · 29th November 2023
Introduction
In Australia, the adoption of solar panels has significantly increased in recent years. This shift towards sustainable energy is positive.
It also brings the need to consider the full life cycle of these panels, particularly their disposal and recycling.
This article explores Australia’s approach to managing end-of-life solar panels. Ensuring a responsible and sustainable use of solar technology.
The Importance of Recycling in the Solar Industry
The growth in solar panel usage brings a crucial responsibility: the proper recycling of old panels. Recycling is essential for several reasons.
Firstly, it allows the recovery of valuable materials like silver and silicon, reducing the need for new raw materials.
This is not only efficient but also lessens the environmental impact associated with mining and processing new resources.
Recycling helps prevent the release of hazardous substances, such as lead, into the environment. Proper recycling processes ensure that these materials are handled safely, protecting the ecosystem.
This consideration is especially vital in Australia. It’s where environmental preservation is a key concern.

Composition of Solar Panels
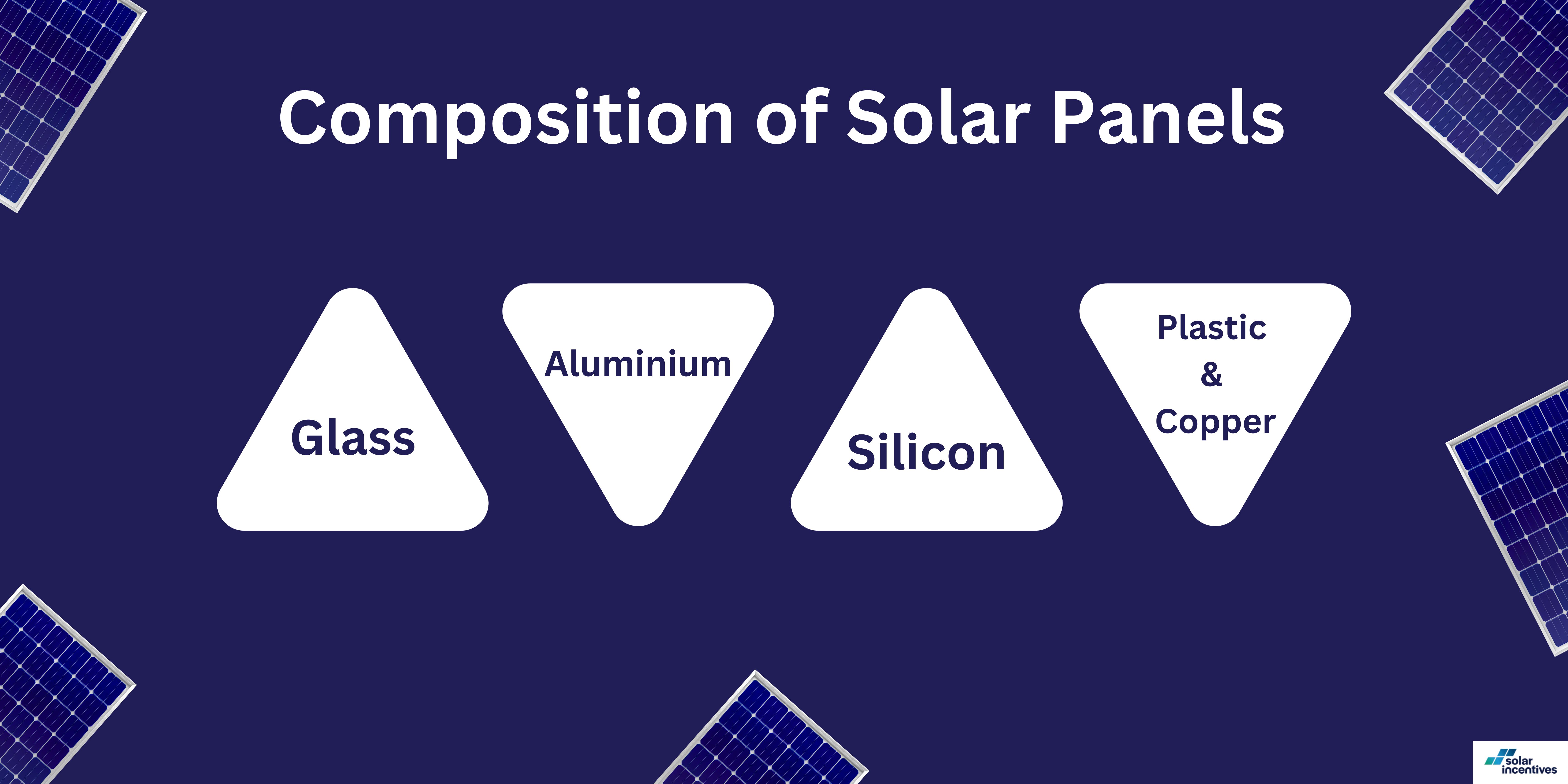
Solar panels are made up of several different materials. Each of these materials plays a part in how the panels work and also in how they can be recycled.
Here’s a closer look at what’s inside a solar panel and why it matters:
Glass
This makes up the largest portion of most solar panels. Glass is highly recyclable, which is good news for recycling efforts.
Aluminium
Often used in the frames of solar panels, aluminium is another material that’s easily recycled. It adds to the durability of the panels but can be reclaimed and reused when the panel’s life ends.
Silicon
This is the key component in most solar panels that actually turns sunlight into electricity. Recycling silicon can be more complex, but it’s crucial because it’s a valuable resource.
Plastic and Copper
These materials are used in the wiring and backing of solar panels. While plastic recycling can be challenging, copper is highly sought after and readily recyclable.
Understanding the mix of materials in solar panels is important. It shows us both the opportunities and the challenges in recycling.
Glass and aluminium can be recycled relatively easily. Plastic and silicon need more specialised processes.
This variety in materials means we need a range of recycling methods to handle everything a solar panel contains.
Recycling Process
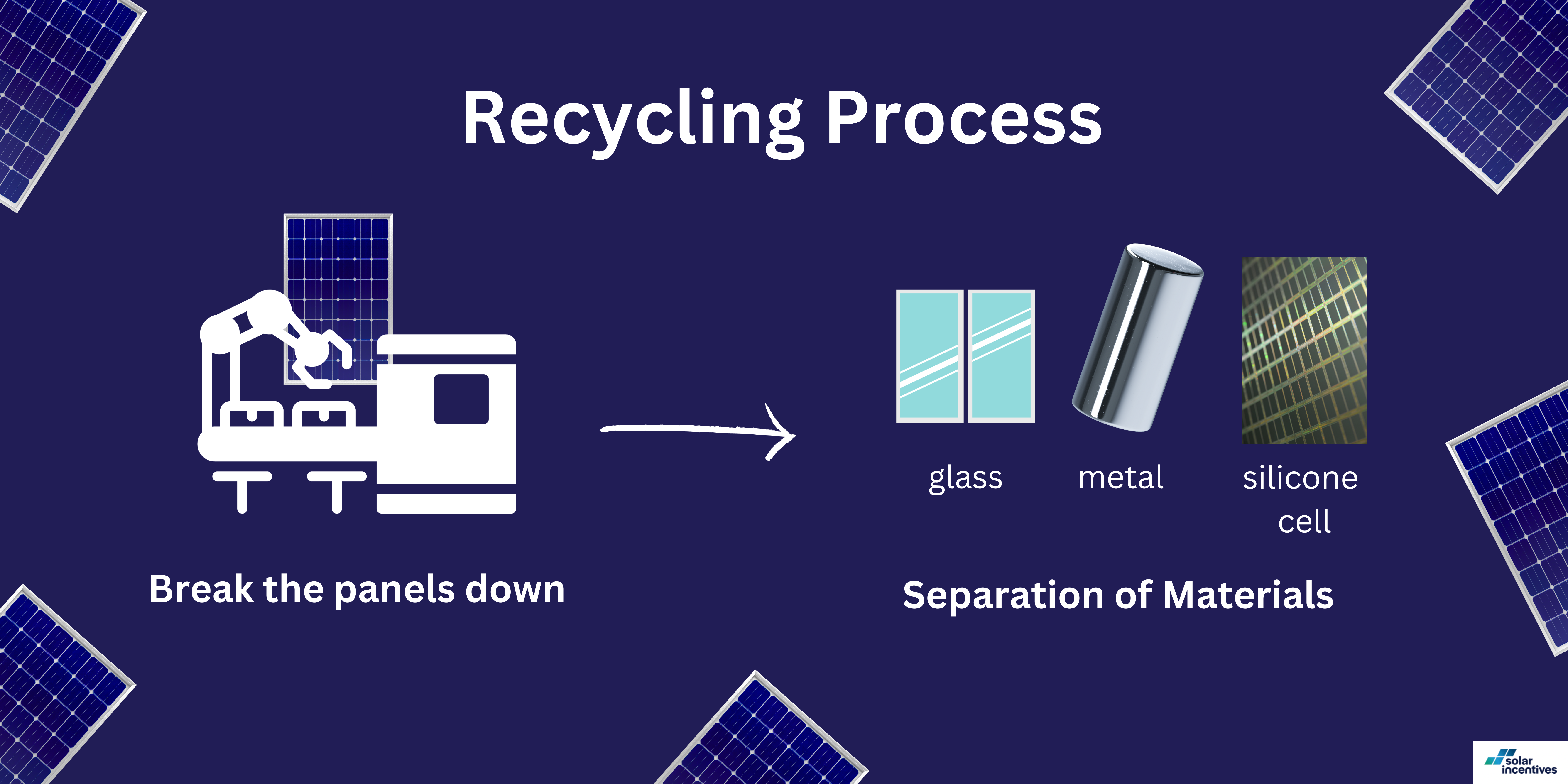
Recycling solar panels is a detailed process with several key steps. It’s not just about taking the panels apart; it’s about doing it in a way that we can use all the different materials again. Here’s how it typically works:
Breaking Down Panels
The first step is to break the panels down. This is done using methods like crushing, shredding, and milling. It’s a bit like taking a complex machine apart so that we can see all the different pieces.
Separation of Materials
After the panels are broken down, the different materials are separated. This step is really important because each material needs to be handled in its own way. Here’s what happens to some of the key materials:
Glass
The glass is often cleaned and prepared for recycling, making it ready to be used in new products.
Metals (like aluminium and copper)
These are separated and sent to metal recyclers. They can be melted down and used to make all sorts of new products.
Silicon cells
These require more careful handling. They’re processed to remove any impurities. It’s making the silicon ready for reuse in new solar panels or other silicon-based products.
This separation process is crucial because it means we can recycle the materials in existing industries.
For example, the glass and metals can go into making new solar panels or other products, reducing the need to mine and process new raw materials.
Recycling Facilities in Australia
Australia is at the forefront of developing efficient solar panel recycling facilities. These facilities play a crucial role in the sustainability efforts of the solar industry.
Let’s explore some of the key players and developments in this field:
Lotus Energy in Thomastown, Victoria
This facility, located a short drive north of Melbourne’s CBD. It is a significant step in Australia’s solar recycling capabilities.
Lotus Energy claims to recycle 100% of end-of-life solar power systems. This including inverters, cables, and mounting structures, using a chemical-free process.
Reclaim PV Recycling in Lonsdale, South Australia
Scheduled to open in Adelaide, this facility marks a major advancement in solar recycling. It will provide a comprehensive solution for recycling end-of-life solar panels. It will establish several drop-off locations across the country. Making it easier for Australians to recycle their old panels.
Reclaim PV aims to recycle 70,000 solar panels in its first year using thermal deconstruction methods. This is like Pyrolysis to recover valuable materials.
AGL’s Initiative with Solar Recovery Corp. (SRC)
AGL, an Australian energy major, is collaborating with SRC. It’s potentially establish a solar panel recycling facility at the Loy Yang power station site in Victoria.
This facility aims to remanufacture end-of-life solar panels. It is part of AGL’s transformation of the Loy Yang site into a low-carbon industrial energy hub.
Other Notable Facilities
There are additional facilities like WA Solar Recycling in Western Australia and PV Industries in New South Wales. These companies contribute to keeping solar panels and system components out of landfills by finding new ways to repurpose and recycle them.
Challenges in Solar Panel Recycling
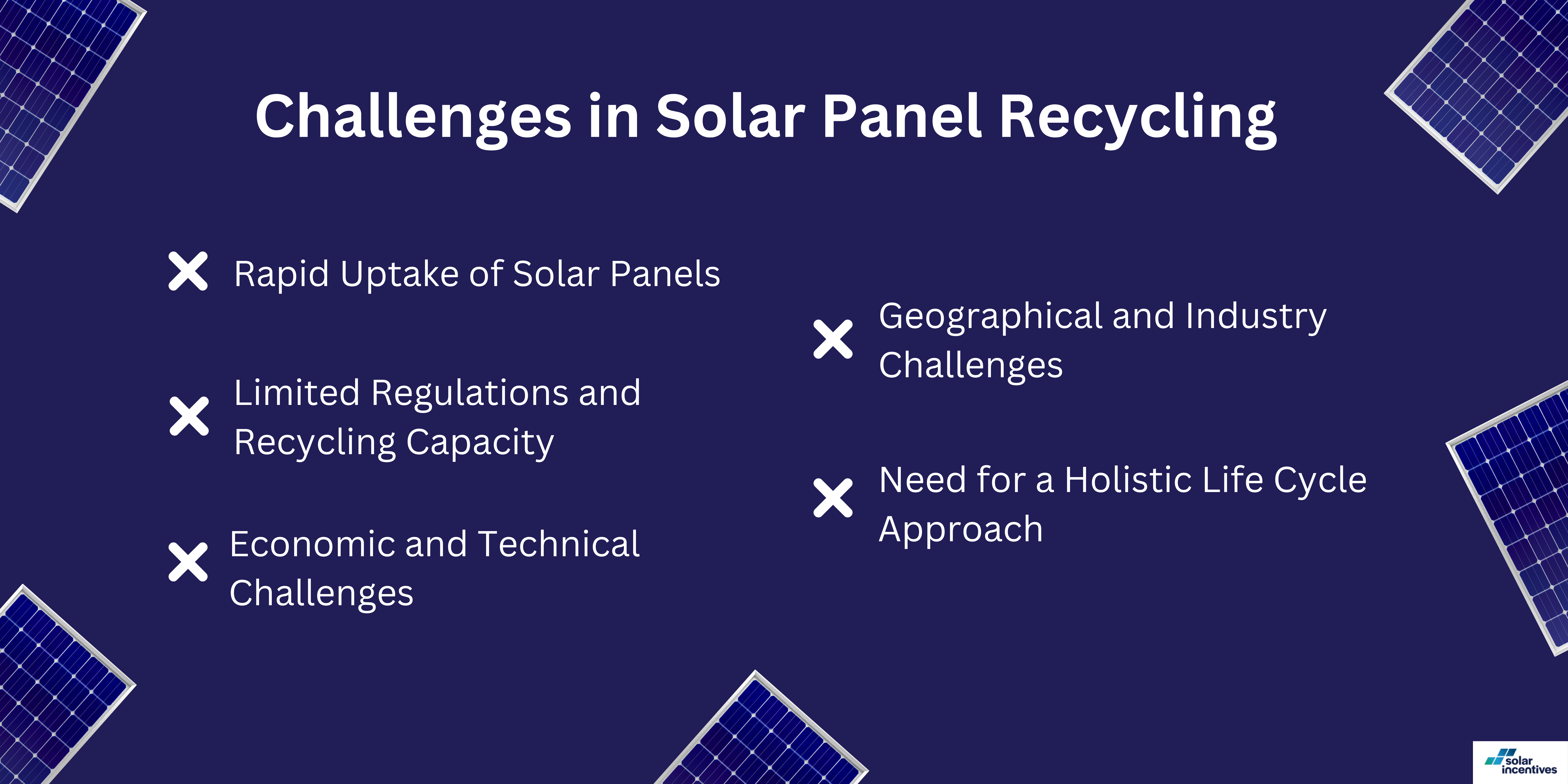
Despite having established recycling facilities, Australia faces significant challenges in solar panel recycling.
These challenges stem from the rapid adoption of solar panels and the complexities involved in the recycling process. Here are some key points to consider:
Rapid Uptake of Solar Panels
Australia leads the world in residential rooftop solar installation, with an adoption rate ten times the global average.
Over 3.3 million Australian homes have solar panels, many of which are now reaching the end of their lifespan.
Limited Regulations and Recycling Capacity
Currently, Australia lacks comprehensive regulations and sufficient domestic recycling capabilities for solar panels. As a result, up to 90 percent of photovoltaic solar panels end up in landfills as toxic hazardous waste.
Economic and Technical Challenges
Recycling a solar panel in Australia costs approximately $28, which is about six times more expensive than sending it to landfill.
This high cost reflects the technical difficulties and labour-intensive nature of the recycling process, as well as the low value of the materials recovered.
Geographical and Industry Challenges
Australia’s situation is complicated by factors like long distances for shipping panels overseas for recycling, high transportation costs from remote areas, and a high turnover of foreign solar manufacturers and importers due to the absence of a domestic solar manufacturing industry.
Need for a Holistic Life Cycle Approach
Experts suggest that Australia should shift from focusing solely on the uptake of renewable technologies to adopting a more comprehensive lifecycle approach.
This approach would encompass recycling and critical mineral recovery at the end of the solar panels’ life, aligning with energy regulation principles.
These challenges highlight the need for Australia to develop more robust strategies and regulations to manage the solar panel life cycle effectively.
The Future of Solar Panel Recycling
As we look forward, the solar panel recycling industry in Australia is poised for significant advancements.
The industry’s commitment to sustainability is evident, with ambitious goals and innovative approaches being developed. Here are some key developments shaping the future:
Comprehensive Product Stewardship
A study by the University of South Australia proposes a product stewardship scheme for solar panels, emphasising the need for incentives for producers to design easily recyclable panels.
Legislative Advances and Landfill Bans
Following the example of some European countries, landfill bans are in place in Victoria. It’s encouraging manufacturers to consider recyclable materials in solar panel production.
Similar legislation for solar panels, akin to that for electric car manufacturers in Europe, is also being discussed.
Environmental and Economic Potential
The recycling of solar panels is not just environmentally critical but also economically promising. With billions of solar panels installed globally, containing valuable high-grade silicon, recycling has the potential to be commercially viable.
Creating a Second-Hand Economy
There is potential for a second-hand economy for solar panels that are still functional. Such a system would need proper legislative support and consumer guarantees for the efficacy of second-hand panels.
Conclusion
In Australia, the effective recycling of solar panels is a key part of our journey towards sustainable energy. As we continue to embrace solar power, it’s vital to develop strong recycling processes and facilities.
This commitment is more than just about reducing environmental impact; it strengthens Australia’s role as a leader in sustainable energy solutions.
Ready to be part of Australia’s clean energy revolution? Discover the right solar solutions for you with Solar Incentives. We’ll help you cut down your electricity bills and enhance your energy security.
Learn more about government incentives for renewable energy and start your journey towards a greener future. Visit us and explore your options through our 2025 Solar Program.
Article By
Steve Hill
Steve Hill has a rich background in the solar energy sector and is dedicated to empowering consumers with knowledge, particularly in residential and commercial solar solutions, solar batteries, and energy efficiency products.
Steve enjoys sharing his wealth of experience, offering practical advice, and learning about the latest trends and innovative solutions in the world of solar energy.

